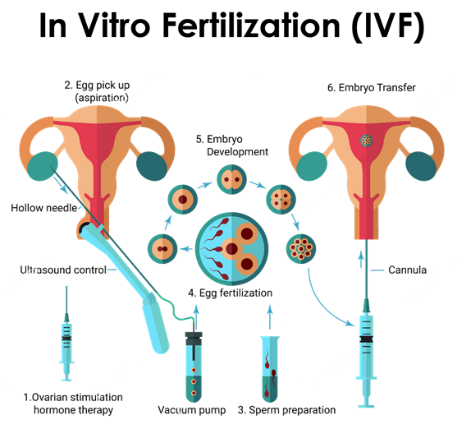
In vitro fertilization, or IVF, is the most common and effective type of assisted reproductive technology to help women become pregnant.
It involves fertilizing an egg outside the body, in a laboratory dish, and then implanting it in a woman’s uterus.
IVF has been used since the late 1970s. On 25 July 1978, the first “test-tube baby,” Louise Brown, was born. Robert Edwards and Patrick Steptoe, who collaborated on the procedure, are considered to be the pioneers of IVF.
In 2010, Robert Edwards received the 2010 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine “for the development of in-vitro fertilization.”
In July 2013, an American couple had the first baby to be born through IVF as a result of next-generation DNA sequencing, a new way of screening embryos that improves IVF success rates and significantly reduces the cost of treatment.
So far, more than 10 million IVF/ICSI and frozen embryo transfer babies have been born throughout the world.
Fast facts about in-vitro fertilization (IVF)
- In-vitro fertilization (IVF) can help achieve pregnancy when other treatments have not worked.
- The process involves fertilizing an egg outside the body, and implanting it to continue the pregnancy.
- One percent of babies born in the United States are conceived through IVF.
- There is a higher chance of a multiple birth with IVF.
DNA sequencing technology helps doctors screen embryos created by IVF to identify those most likely to lead to successful pregnancies.
Candidates
In-vitro fertilization is ideal for women who have not been able to become pregnant through regular unprotected intercourse or after 12 cycles of artificial insemination.
Success rate
In 2016, 26 percent of procedures led to a live birth.
In 2010, the United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS) estimated that the chance of a live birth was:
- 32.2 percent for women aged under 35 years
- 27.7 percent for women aged between 35 to 37 years
- 20.8 percent for women aged between 38 to 39 years
- 13.6 percent for women aged 40 to 42 years
- 5 percent for women aged 43 to 44
- 1.9 percent for women aged over 44 years
These statistics vary depending on where IVF is done.
Other factors that may affect success
Apart from age, the likelihood of success depends on factors including:
- how long you have been trying to become pregnant
- the cause of the infertility
- whether or not pregnancy or a live birth has occurred before
- the strategy that will be used
One study, published in CMAJ Open in 2013, has suggested that women who have sufficient levels of vitamin D are “significantly more likely” to become pregnant with IVF compared with those who have lower levels of this vitamin. It is not known if taking vitamin D supplements can affect your chances of getting pregnant, either naturally or with IVF.
Risks
Some risks are associated with IVF.
Side effects of medication
Share on PinterestIVF can cause difficulty sleeping.
Some women may have reactions to the medications that are given during treatment.
The possible side effects of IVF drugs include:
- nausea and vomiting
- difficulty breathing
- irritability
- hot flashes
- enlargement of the ovaries
- difficulty sleeping
- abdominal pain
Bruising can also result from repeated daily injections.
Health risks to the mother
Rarely, the drugs can cause ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). This happens when the ovaries over-respond to the gonadotrophins, so that too many eggs develop in the ovaries. Severe abdominal swelling and shortness of breath can result. If OHSS occurs, the doctor may suggest restarting the whole cycle with a lower dose of gonadotropin.
Research published in the BMJ has linked IVF with a higher risk of pulmonary embolism, or blockage of the lung’s main artery, and venous thromboembolism, or blood clots, during the 1st trimester of pregnancy.
Pregnancy loss
The leading cause of pregnancy loss, whether in IVF or in natural conception, is an abnormal number of chromosomes, known as chromosomal aneuploidy. Detecting aneuploidy in the egg or sperm before carrying out IVF, or in an embryo before implantation, may help increase the chance of a successful pregnancy.
In 2013, scientists announced that they had developed a new technology called time-lapse imaging. The technique may increase the chances of selecting a suitable embryo for successful IVF, though further research needs to be done.
Multiple Births
When more than one embryo is transferred into the womb, there is a higher chance of having twins, triplets, or more babies.
Pregnancies with more than one fetus can result in:
- preterm birth or low birth weight
- double the mother’s risk of developing diabetes
- significant increase in the mother’s blood pressure
The doctor may recommend that there should only be a single embryo transfer in women with a heightened chance of having twins.
Arogya Finance, a social healthcare venture based in Mumbai’s tying-up with various doctors and hospitals for various medical treatments. Arogya Finance facilitates easy Equated Monthly Instalments to patients to pay for the treatments provided by the doctors and hospitals.
“Unexpected healthcare expenses have led to over 40 million people falling into poverty every year due to heavy expenses incurred for numerous treatments. Arogya Finance has partnerships with various doctors and hospitals to make medical loans available to patients at the right time and place in different parts of India. We are already in talks with many hospitals, pharma companies and major doctors across India to provide a one-stop financial solution for people in need whenever and wherever there is an unforeseen medical emergency.” said Mr. Jose Peter, Co-Founder and CEO of Arogya Finance.
Arogya Finance is here to help the people throughout the country to borrow easily and quickly in times of medical emergencies and how you can secure a loan for your healthcare finance needs where you need no collateral, minimum documentation. Get in touch with us for more details.
SOURCE: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/262798#procedure